Traditional Farming Business Insights
Sustainable,
high-demand farming.
Start a profitable hydroponic farming business with low water usage, high-yield crops, and automation. Sell directly to restaurants, consumers, and grocery stores, or scale through subscriptions, wholesale, and hydroponic system sales.
Traditional Farming Business Insights
Sustainable,
high-demand farming.
Start a profitable hydroponic farming business with low water usage, high-yield crops, and automation. Sell directly to restaurants, consumers, and grocery stores, or scale through subscriptions, wholesale, and hydroponic system sales.
Traditional Farming Business Insights
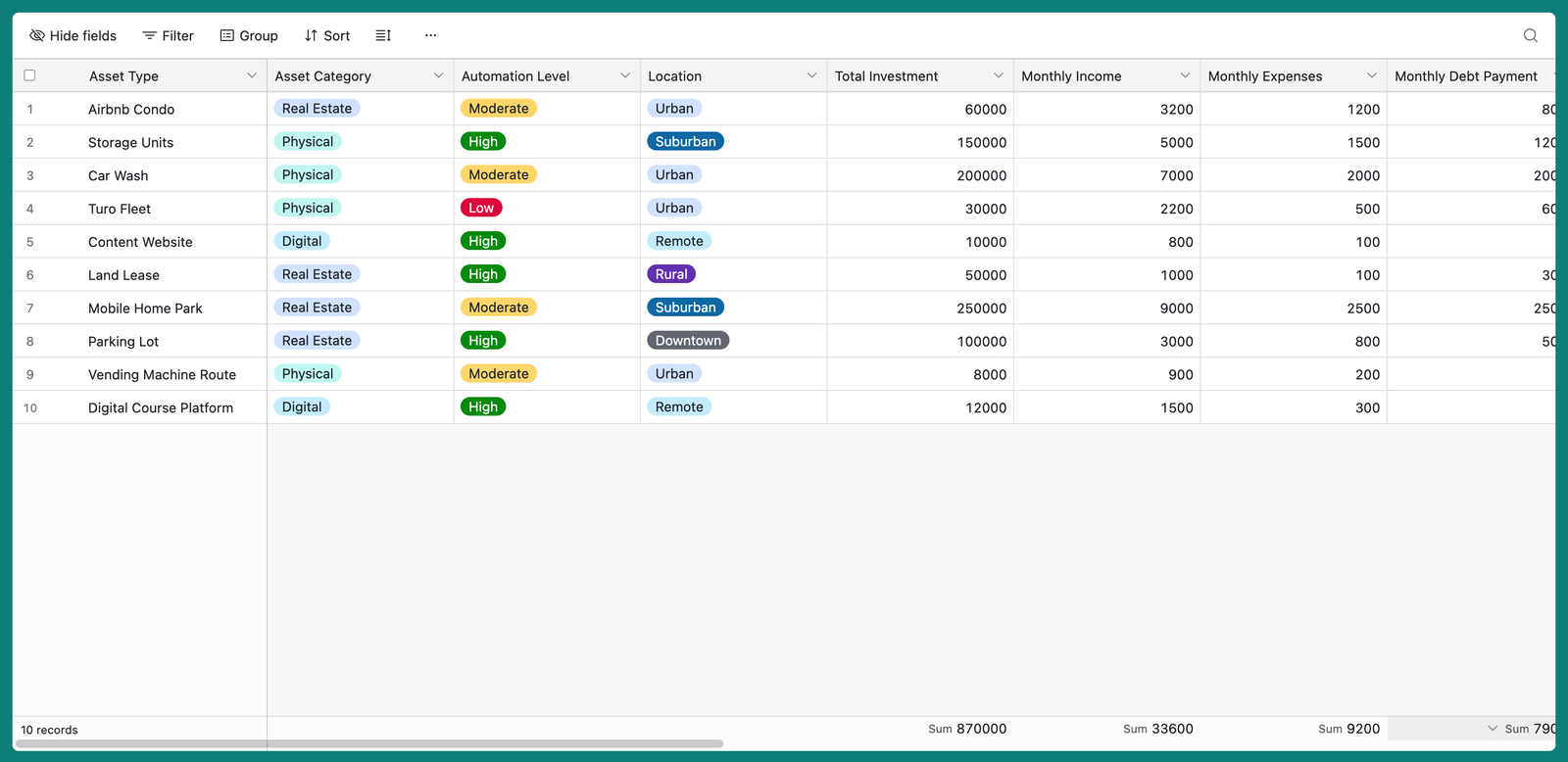
🏆 Overall Business Viability Score
💰 Profitability Score
🚀 Scalability Score
⏳ Time to Profitability Score
💸 Startup Cost Score
🛠️ Operational Complexity Score
📢 Marketing & Customer Acquisition Score
🤖 Automation & Passive Income Score
📈 Market Demand Score
⚠️ Competition Level Score
🌱 Sustainability & Longevity Score
📊 Revenue Stability Score
🏗️ Barrier to Entry Score
🎯 Target Market Size Score
🔧 Skill & Experience Requirement Score
📍 Location Flexibility Score
💼 Legal & Compliance Complexity Score
🔥 Economic Resilience Score
🔄 Recession Proof Score
🏁 Exit Strategy Score
Business Idea Overview:
Traditional farming involves growing crops and raising livestock for commercial sale. With increasing demand for organic and local food, farmers can thrive by diversifying revenue streams, leveraging automation, and adopting sustainable practices.
📊 Earning Potential
⚠️ Earnings Disclaimer: Actual earnings vary based on niche, strategy, and execution. There is no guarantee of success, and results depend on effort, market conditions, and business management.
🛠️ Best Platforms & Tools
Successful farming requires land management tools, precision agriculture software, and supply chain platforms. Key tools include:
- Soil & crop monitoring software for yield optimization
- Farm management platforms for logistics & inventory tracking
- E-commerce & local food marketplaces to sell directly to consumers
⚠️ Biggest Challenge
The biggest challenges include climate unpredictability, rising input costs, and market fluctuations. Farmers must also navigate supply chain disruptions and labor shortages, requiring innovative solutions such as sustainable farming practices and direct-to-consumer sales.
💸 Startup Costs & Investment
Starting costs range from $10K for small-scale operations to millions for commercial farms. Land acquisition, equipment, seeds, labor, and irrigation systems make initial investment high, but grants and farm loans can help reduce financial burdens.
📢 Customer Acquisition Strategy
- Farmers’ Markets & CSA Programs – Selling locally builds strong customer relationships
- Online Farm Stores & E-Commerce – Direct-to-consumer websites increase profitability
- Partnerships with Restaurants & Grocery Stores – Reliable contracts for long-term stability
- Wholesale & Exporting – Large-scale revenue opportunities
📈 Ideal Business Model
Farming can be monetized through:
- One-time sales (direct farm sales, wholesale contracts)
- Recurring revenue (CSA memberships, farm subscriptions)
- High-ticket contracts (exporting specialty crops, organic certifications)
⏳ Time to Profitability
Traditional farming has longer ROI cycles since crops take months (or years) to mature. Expect 1–3 years to reach profitability, depending on farm scale, location, and crop type.
🚀 Key to Scaling
Scaling requires expanding land, implementing automation, and securing distribution channels. Diversifying into value-added products (organic produce, dairy, packaged goods) can increase margins and reduce reliance on volatile crop prices.
🤖 Automation & Passive Income Potential
While farming is hands-on, automated irrigation, AI-driven soil analysis, and drone monitoring reduce manual labor. Passive income streams can include farm tours, online courses, and value-added products.
View Automation Tools
🏁 Exit Strategy
Farm owners can sell land, lease it for passive income, or transition to agritourism. Some choose succession planning for family-run farms or selling to agricultural investment firms.
🌱 Sustainability & Longevity
With increasing demand for organic, regenerative, and sustainable farming, this business has strong long-term potential. Eco-friendly and sustainable practices can enhance profitability and secure government grants or tax incentives.
🔄 Market Trends & Demand
- Rising demand for organic & local produce
- Technological advancements in smart farming & automation
- Increase in direct-to-consumer and farm-to-table business models
- Government incentives for sustainable farming & carbon-neutral practices
🆚 Competition Level
Competition varies by region and niche. Local, organic, and specialty farms face less competition than commodity crop producers.
Sign up for SEO Flow and start your keyword research today. SEOFlow.app
📍 Location Flexibility
Farming requires physical land, but distribution models (e.g., e-commerce, CSA boxes, direct-to-consumer) allow farmers to reach wider markets.
Visit NomadWave’s Digital Nomad Community
🎯 Ideal Target Audience
- Local consumers looking for organic or farm-fresh produce
- Restaurants, grocery stores, and wholesalers
- Farm-to-table businesses & meal kit services
- Eco-conscious consumers supporting sustainable farms
🏗️ Operational Complexity
Traditional farming is labor-intensive and requires knowledge of soil health, irrigation, pest management, and supply chain logistics.
🔧 Required Skills & Experience
- Agricultural knowledge (crop management, soil health, livestock care)
- Supply chain & logistics for distribution efficiency
- Marketing & branding for direct-to-consumer sales
- Sustainable farming techniques for long-term profitability
💼 Legal & Compliance Considerations
- Land & water rights regulations
- Organic & sustainable farming certifications
- Food safety & storage laws
- Labor laws for seasonal workers
📊 Best Monetization Strategies
- Selling fresh produce & livestock
- Farm subscription services (CSA boxes, meat deliveries)
- Agri-tourism & educational farm experiences
- Selling value-added products (jams, honey, dairy, canned goods)
🔥 Recession & Economic Resilience
Food is a necessity, making farming relatively recession-proof. However, farmers must diversify crops, reduce reliance on single distributors, and adopt tech-driven efficiency to stay profitable.
💰 Earning Potential in Traditional Farming Business
The earning potential of a traditional farming business varies widely depending on factors such as farm size, crop selection, livestock, market access, and operational efficiency.
Average Income & Profit Margins:
- Small farms can generate $20,000 – $100,000 per year, with many relying on additional income sources.
- Mid-sized farms can bring in $100,000 – $500,000 annually, depending on crop yields and distribution strategies.
- Large-scale farms have the potential to earn millions annually, especially when selling to wholesale markets, restaurants, or processing plants.
- Profit margins typically range between 10-30%, depending on the cost of production and sales strategy.
Key Factors That Impact Earnings:
✅ Farm Type & Products – Cash crops (corn, wheat, soy) have lower profit margins, while organic produce, specialty crops, and livestock can generate higher earnings.
✅ Land Ownership vs. Leasing – Owning land reduces long-term costs, while leasing increases operational expenses but allows flexibility.
✅ Direct-to-Consumer Sales – Selling at farmers’ markets, CSAs, or through e-commerce can increase profits by cutting out middlemen.
✅ Value-Added Products – Turning raw products into items like organic juices, dairy products, or packaged goods boosts revenue potential.
✅ Sustainability & Niche Markets – Organic, regenerative, and farm-to-table trends can lead to premium pricing and customer loyalty.
✅ Government Grants & Subsidies – Many regions offer financial assistance to support local farms, improving profitability.
Challenges to Profitability:
⚠️ Weather & Climate Risks – Droughts, floods, and changing climate conditions impact crop yields.
⚠️ High Startup & Operational Costs – Land, equipment, seeds, feed, and labor require substantial investment.
⚠️ Fluctuating Market Prices – Commodity prices are volatile and can affect revenue unpredictably.
⚠️ Labor & Management – Managing workers, seasonal labor shortages, and compliance with regulations add to costs.
How to Maximize Earnings in Farming:
🚀 Diversify Income Streams – Combine crop farming, livestock, agritourism, and value-added products.
🚀 Leverage E-Commerce & Direct Sales – Build a brand and sell online or directly to restaurants and consumers.
🚀 Use Smart Farming & Technology – Improve efficiency with automation, hydroponics, precision agriculture, and AI-driven monitoring.
🚀 Secure Contracts & Partnerships – Selling directly to retailers, co-ops, or meal delivery services ensures steady income.
Final Verdict:
Traditional farming can be highly profitable but requires strategic planning, investment, and risk management. Farmers who embrace modern techniques, direct sales, and sustainability trends can significantly increase their earning potential. 🌱🚜
⚠️ Earnings Disclaimer: Actual earnings vary based on niche, strategy, and execution. There is no guarantee of success, and results depend on effort, market conditions, and business management.
📈 Best Business Models for a Traditional Farming Business
A traditional farming business can adopt various business models depending on available resources, target markets, and scalability goals. Choosing the right approach can maximize profitability, reduce risks, and improve sustainability. Below are the most effective business models for a farming business.
1️⃣ Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Farming
💰 Revenue Model: Selling directly to consumers via farmers’ markets, CSA (Community Supported Agriculture) programs, and online farm stores.
🔹 How It Works:
- Customers buy fresh produce, dairy, meat, or specialty products directly from the farm.
- Subscription-based CSA programs allow consumers to prepay for weekly or seasonal farm shares.
- Farmers’ markets and online stores provide a premium pricing advantage by eliminating middlemen.
✔ Best For: Small and medium-sized farms with organic or specialty produce.
⚠ Challenges: Requires strong marketing, logistics, and customer retention strategies.
2️⃣ Wholesale Farming (B2B Model)
💰 Revenue Model: Selling crops, livestock, or dairy to grocery stores, restaurants, or food manufacturers.
🔹 How It Works:
- Farms produce in bulk and sign supply contracts with restaurants, supermarkets, or food distributors.
- Cooperative farming groups pool resources to fulfill larger wholesale demands.
✔ Best For: Large-scale farms with high-yield crops and livestock.
⚠ Challenges: Lower profit margins, dependency on contracts, and price fluctuations.
3️⃣ Value-Added Farming (Product Processing & Branding)
💰 Revenue Model: Processing raw products into high-margin items like organic jams, cheese, fresh juices, or meal kits.
🔹 How It Works:
- Farmers process, brand, and sell their products instead of just raw produce.
- Value-added products allow for premium pricing and branding opportunities.
- Can be sold online, in local stores, or via subscriptions (e.g., farm-to-table meal kits).
✔ Best For: Farms with unique or organic produce, dairy, or specialty crops.
⚠ Challenges: Requires additional certifications, processing facilities, and marketing efforts.
4️⃣ Agritourism & Farm Experiences
💰 Revenue Model: Charging for farm visits, workshops, U-Pick experiences, and eco-tourism activities.
🔹 How It Works:
- Farms create tourist attractions such as pumpkin patches, petting zoos, vineyard tours, and farm-to-table events.
- Visitors pay for experiences like fruit picking, farm stays, or educational tours.
✔ Best For: Farms in high-tourism areas with scenic landscapes or unique experiences.
⚠ Challenges: Requires permits, liability management, and infrastructure investments.
5️⃣ Contract Farming & Government Partnerships
💰 Revenue Model: Pre-arranged contracts with corporations, government agencies, or agribusinesses.
🔹 How It Works:
- Large-scale farms grow crops or raise livestock under contracts with food processing companies.
- Governments provide grants, subsidies, or incentives to support local food production.
✔ Best For: Farms producing staple crops, biofuels, or medicinal plants.
⚠ Challenges: Requires long-term commitment, strict compliance, and pricing negotiations.
6️⃣ Farm Leasing & Land Investment Model
💰 Revenue Model: Leasing out farmland to agribusinesses, startups, or beginner farmers.
🔹 How It Works:
- Farm owners lease unused land for organic farming, solar farms, or sustainable projects.
- Real estate investors buy farmland and lease it to farmers or agritech companies for passive income.
✔ Best For: Large landowners looking for low-maintenance revenue.
⚠ Challenges: Requires long-term leasing agreements and land-use management.
7️⃣ Sustainable & Organic Farming (Premium Market Model)
💰 Revenue Model: Selling organic, regenerative, or sustainably farmed produce at premium prices.
🔹 How It Works:
- Farms certify as organic or regenerative to target health-conscious consumers.
- Products are sold at higher price points in specialty stores, online, or through direct-to-consumer sales.
✔ Best For: Small farms with a focus on niche, premium markets.
⚠ Challenges: Certification costs and strict regulatory requirements.
💡 Final Verdict: Best Business Models for Traditional Farming
✅ Most Profitable: Value-Added Farming, Direct-to-Consumer, and Sustainable Organic Farming.
✅ Best for Scaling: Wholesale, Contract Farming, and Farm Leasing.
✅ Most Passive: Farm Leasing, Government Contracts, and Agritourism.
✅ Best for Local Markets: Direct-to-Consumer, Agritourism, and Farm Branding.
Choosing the right business model depends on farm size, market demand, and long-term growth strategy. 🚜🌱
Get JotPro, the intuitive AI writing tool with over 50 templates, and countless features like Speech-to-Text and Text-to-Speech. Sign Up Free
📢 Marketing Strategies for a Traditional Farming Business
A traditional farming business requires a strong marketing strategy to attract customers, build brand loyalty, and maximize sales. Whether selling directly to consumers, partnering with distributors, or leveraging online platforms, a well-rounded marketing approach can boost profitability and sustain long-term growth. Below are proven marketing strategies tailored to the farming industry.
1️⃣ Local & Community-Based Marketing (Best for Direct Farm Sales)
🔹 Farmers’ Markets & Local Events
- Set up booths at farmers’ markets, food fairs, and community events to showcase products.
- Offer samples, bundle deals, and subscription discounts to attract repeat buyers.
🔹 Partnerships with Local Restaurants & Stores
- Supply organic produce, dairy, or meat to restaurants, cafes, and grocery stores.
- Collaborate on farm-to-table menus and promotions for added exposure.
🔹 CSA (Community Supported Agriculture) Programs
- Sell seasonal produce subscriptions to local households, ensuring consistent revenue.
- Use referral incentives to encourage word-of-mouth marketing.
✅ Best For: Direct-to-consumer farms, organic & sustainable produce, local food sales.
2️⃣ Content Marketing & SEO (Best for Online Growth & Lead Generation)
🔹 Educational Blog & SEO-Optimized Website
- Publish farming tips, sustainability guides, and recipe blogs to attract organic search traffic.
- Optimize posts for keywords like “buy organic farm products” or “local farm fresh eggs.”
🔹 Email Marketing & Newsletters
- Send weekly farm updates, seasonal produce lists, and discounts to subscribers.
- Offer a lead magnet (free guide on organic farming or recipes) to grow the email list.
🔹 Google My Business & Local SEO
- List the farm on Google My Business, Yelp, and local directories to rank for nearby searches.
- Encourage customer reviews & testimonials to improve search rankings.
✅ Best For: Farms with e-commerce, CSA subscriptions, and farm tours.
3️⃣ Social Media & Video Marketing (Best for Brand Awareness & Engagement)
🔹 Instagram & TikTok for Visual Content
- Post farm-to-table meal ideas, behind-the-scenes farm life, and harvesting videos.
- Use trending hashtags (#FarmLife, #OrganicFood, #SustainableFarming) to reach a broader audience.
🔹 YouTube & Short-Form Video Content
- Create educational videos on farming techniques, food preservation, and DIY gardening.
- Promote farm products by sharing customer testimonials & cooking demonstrations.
🔹 Facebook Groups & Community Engagement
- Join local foodie & sustainability groups to share farm updates.
- Host live Q&A sessions about organic farming, sustainable agriculture, and farm tours.
✅ Best For: Increasing brand awareness, attracting farm visitors, and engaging new customers.
4️⃣ Influencer & Affiliate Marketing (Best for Expanding Reach)
🔹 Collaborate with Food & Wellness Influencers
- Partner with chefs, nutritionists, and food bloggers to showcase farm products.
- Offer affiliate commissions for influencers who drive sales.
🔹 Cross-Promotions with Other Local Businesses
- Work with bakeries, coffee shops, and organic meal delivery services for co-branded promotions.
- Offer bundled farm-to-table meal kits in collaboration with local chefs.
🔹 Affiliate & Referral Programs
- Incentivize loyal customers & social media followers with referral bonuses for new subscribers.
✅ Best For: Premium farm products, organic produce, and farm subscription boxes.
5️⃣ Paid Advertising & Online Marketplaces (Best for Rapid Sales Growth)
🔹 Facebook & Instagram Ads
- Run geo-targeted ads to attract local buyers.
- Use video ads showcasing farm tours, produce harvesting, and cooking tutorials.
🔹 Google Shopping & PPC Ads
- List fresh produce, dairy, and farm goods on Google Shopping & search ads.
- Target high-intent keywords like “buy farm-fresh eggs near me.”
🔹 Etsy, Amazon Fresh & E-Commerce Sales
- Sell homemade jams, organic honey, farm-themed merchandise, and specialty farm products on Etsy & Amazon.
- Optimize listings with high-quality images and SEO-friendly descriptions.
✅ Best For: Scaling online sales, reaching new customers, and increasing product visibility.
📊 Marketing Strategy Comparison Table
| Strategy | Best For | Cost | Traffic Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local & Community Marketing | Direct farm sales, CSA subscriptions | Low | High (Word-of-mouth) |
| SEO & Content Marketing | Farms with blogs, farm tours, e-commerce | Low-Medium | High (Long-term) |
| Social Media & Video | Brand awareness, organic farming education | Free or Paid | Very High (Viral potential) |
| Influencer & Affiliate Marketing | Expanding reach, premium products | Medium | High (Trust-based sales) |
| Paid Ads & Marketplaces | Rapid growth, online farm product sales | Medium-High | High (Immediate sales) |
📌 Final Verdict: Best Marketing Strategies for Traditional Farming
✅ Best Long-Term Strategy: SEO, Blogging, Local Marketing, CSA Subscriptions
✅ Best for Fast Sales: Paid Ads, E-Commerce Listings, Influencer Promotions
✅ Best for Brand Awareness: Social Media, Video Marketing, Farm Tours
✅ Best for Passive Marketing: Affiliate Programs, Referral Marketing, Email Marketing
A multi-channel approach combining local sales, online branding, and strategic partnerships is key to sustainable growth in the farming business. 🚜🌿
🎯 Conversion Tactics for a Traditional Farming Business
Converting visitors into paying customers is crucial for a traditional farming business, whether selling directly to consumers, supplying to businesses, or running an online farm store. Implementing effective conversion tactics ensures higher sales, repeat customers, and increased revenue. Below are the best conversion strategies for farmers and agricultural entrepreneurs.
1️⃣ Clear & Persuasive Product Descriptions (Boosts Sales & Trust)
🔹 Highlight Freshness & Quality
- Use descriptive, sensory language to emphasize the freshness, taste, and nutritional benefits of your produce.
- Example: Instead of “Fresh Strawberries,” write “Handpicked, sun-ripened strawberries bursting with sweetness and natural antioxidants.”
🔹 Transparent Sourcing & Farming Methods
- Educate customers on organic practices, pesticide-free farming, or regenerative agriculture to build trust.
- Include “Farm-to-Table” stories to show authenticity and differentiate from supermarkets.
🔹 Certifications & Awards
- Display organic, fair-trade, or non-GMO certifications to increase credibility and buyer confidence.
✅ Best For: Direct-to-consumer farms, farm subscription boxes, e-commerce stores.
2️⃣ Offer Bundled Deals & Subscriptions (Encourages Larger Purchases)
🔹 Create “Harvest Boxes” or CSA Subscription Plans
- Offer weekly or monthly fresh produce bundles at a discounted price for recurring customers.
- Incentivize sign-ups with free first delivery or bonus farm-fresh products.
🔹 Cross-Sell Complementary Items
- Suggest related products:
- 🥩 “Buy fresh eggs? Get a discount on pasture-raised chicken!”
- 🍯 “Pair organic honey with our farm-fresh herbal tea!”
🔹 Volume Discounts
- Encourage bulk purchases by offering tiered discounts:
- “Buy 2, Get 1 Free” for seasonal produce.
- “Save 15% on orders over $50.”
✅ Best For: Increasing cart value in farm stores, CSA programs, and wholesale buyers.
3️⃣ Leverage Social Proof & Customer Testimonials (Builds Trust & Authority)
🔹 Feature Reviews & User-Generated Content
- Showcase real customer testimonials, photos, and farm visit experiences on your website & social media.
- Display ratings and reviews to establish credibility.
🔹 Collaborate with Local Chefs & Restaurants
- Share chef testimonials using farm products in their dishes.
- Create recipes featuring your farm ingredients to inspire customers.
🔹 Before & After Stories
- Show customers how fresh, local produce improves health, taste, and quality of life.
✅ Best For: Increasing customer confidence in organic and sustainable farm products.
4️⃣ Limited-Time Offers & Seasonal Scarcity (Creates Urgency)
🔹 Seasonal Specials & Flash Sales
- Offer limited-time discounts on seasonal crops, dairy, or meat to encourage immediate purchases.
- Example: “Only 100 boxes of fresh summer peaches left! Order now before they’re gone!”
🔹 Early Bird Discounts for CSA Sign-Ups
- Reward customers who subscribe before the season starts with special pricing or bonus products.
🔹 Exclusive Harvest Pre-Orders
- Allow loyal customers to reserve fresh produce in advance, ensuring guaranteed sales.
✅ Best For: Driving fast conversions & increasing seasonal sales.
5️⃣ Optimize Checkout Process & Payment Flexibility (Reduces Cart Abandonment)
🔹 Easy One-Page Checkout
- Ensure a quick, seamless checkout experience to prevent drop-offs.
- Offer guest checkout so customers don’t need to create an account.
🔹 Multiple Payment Options
- Accept credit/debit cards, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services to remove purchasing barriers.
🔹 Free or Discounted Local Delivery
- Provide free delivery for orders above a certain amount to incentivize larger purchases.
- Offer local pickup options for nearby customers.
✅ Best For: Reducing friction & improving farm store conversions.
6️⃣ Email & Retargeting Campaigns (Re-Engages & Converts Customers)
🔹 Abandoned Cart Email Reminders
- Send friendly reminders like “You left fresh farm eggs in your cart – complete your order before they sell out!”
🔹 Exclusive Offers for Past Customers
- Reward previous buyers with loyalty discounts or VIP farm event invitations.
🔹 Retargeting Ads on Facebook & Google
- Show targeted ads to past visitors reminding them of seasonal farm produce and limited-time deals.
✅ Best For: Converting undecided customers & boosting repeat sales.
7️⃣ Farm Events & Experiential Marketing (Creates Brand Loyalty)
🔹 Host Farm-to-Table Dinners & Workshops
- Invite customers to exclusive farm dinners, cooking classes, or farm tours.
- Sell event tickets or premium farm memberships for recurring revenue.
🔹 Virtual Farm Tours & Live Q&A Sessions
- Engage your audience with behind-the-scenes farm videos and live cooking demonstrations.
✅ Best For: Strengthening customer relationships & increasing lifetime value.
📊 Conversion Tactics Comparison Table
| Conversion Tactic | Best For | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Persuasive Product Descriptions | E-Commerce, Farm Stores | High |
| Bundled Deals & Subscriptions | CSA Programs, Online Farm Shops | Very High |
| Social Proof & Testimonials | Premium Farm Products, Organic & Sustainable Goods | High |
| Seasonal Scarcity & Flash Sales | Farm Direct Sales, Subscription Sign-Ups | Medium-High |
| Easy Checkout & Payment Flexibility | Online & Local Farm Sales | High |
| Email & Retargeting Campaigns | Farm Stores, Recurring Buyers | High |
| Farm Events & Brand Loyalty | CSA Memberships, Premium Farm Experiences | High |
📌 Final Verdict: Best Conversion Tactics for Farming Businesses
✅ Best for Immediate Sales: Seasonal scarcity, limited-time offers, social proof
✅ Best for Recurring Revenue: Subscription models, CSA programs, bundled deals
✅ Best for Brand Loyalty: Farm events, VIP memberships, personalized customer engagement
✅ Best for Reducing Cart Abandonment: Optimized checkout process, multiple payment options
A multi-layered approach combining scarcity, subscription-based sales, strong branding, and seamless checkout will increase conversions and long-term farm profitability. 🚜🌱
💰 Most Profitable Niches in Traditional Farming Business
Farming is a broad industry with multiple revenue opportunities, but not all niches are equally profitable. Certain farming models offer higher margins, scalability, and sustainable long-term income. Below are the most profitable traditional farming niches based on market demand, scalability, and revenue potential.
1️⃣ Organic & Specialty Crop Farming (High-Demand, Premium Pricing)
🔹 Why It’s Profitable
- Consumers are increasingly choosing organic and non-GMO foods, leading to premium pricing.
- Government subsidies and incentives for organic farming help reduce costs.
- Farmers’ markets, restaurants, and subscription boxes drive strong demand.
🔹 Best-Selling Organic Crops
✅ Leafy greens, microgreens, heirloom tomatoes, garlic, ginger, turmeric, lavender, specialty herbs.
🔹 Profit Potential
💰 High – Organic products sell for 30-50% more than conventional alternatives.
✅ Best For: Small to mid-sized farms, urban farmers, direct-to-consumer sales.
2️⃣ Livestock Farming & Free-Range Animal Products (Sustainable & Recurring Revenue)
🔹 Why It’s Profitable
- Grass-fed, free-range, and organic meats and dairy command premium prices.
- Eggs, milk, meat, and wool provide multiple revenue streams.
- Subscription models (CSA, farm memberships) ensure steady cash flow.
🔹 Most Profitable Livestock Niches
✅ Grass-fed beef, pastured poultry, heritage pork, organic dairy, free-range eggs, and specialty wool.
🔹 Profit Potential
💰 High – Specialty animal products sell for 2-3x more than conventional options.
✅ Best For: Farmers with land and experience in animal care, regenerative agriculture.
3️⃣ Medicinal & Herbal Farming (Evergreen & Growing Demand)
🔹 Why It’s Profitable
- Health-conscious consumers are spending more on herbal teas, tinctures, and supplements.
- Direct-to-consumer sales and herbal wellness products increase profit margins.
- Less competition compared to traditional crops.
🔹 Best-Selling Herbal & Medicinal Crops
✅ Ginseng, lavender, echinacea, chamomile, valerian root, peppermint, lemon balm, turmeric.
🔹 Profit Potential
💰 High – Medicinal plants and essential oils sell for $20–$100 per pound.
✅ Best For: Small farms, value-added product sellers, online herbal shops.
4️⃣ Greenhouse & Controlled Environment Farming (Year-Round Profitability)
🔹 Why It’s Profitable
- Enables year-round growing, even in cold climates.
- Faster growth cycles and better pest control = more profitable harvests.
- High-value crops (tomatoes, strawberries, peppers) yield strong returns.
🔹 Best Crops for Greenhouse Farming
✅ Lettuce, peppers, strawberries, cucumbers, cannabis, microgreens, edible flowers.
🔹 Profit Potential
💰 Very High – Controlled environments yield higher ROI per acre.
✅ Best For: Farmers with greenhouse space, urban agriculture, high-margin crops.
5️⃣ Agritourism & Farm Experiences (Multiple Income Streams)
🔹 Why It’s Profitable
- Combines tourism with farming, attracting visitors for farm tours, workshops, and events.
- Multiple revenue streams: entrance fees, workshops, farm stays, product sales.
- Higher margins than just selling crops or livestock.
🔹 Most Profitable Agritourism Models
✅ Farm-to-table dinners, petting zoos, farm wedding venues, wine or cider tastings, pumpkin patches.
🔹 Profit Potential
💰 Very High – Agritourism can generate 2-5x more income than traditional crop sales alone.
✅ Best For: Farmers near cities or tourist areas, those looking for diversified income.
6️⃣ Nut & Tree Farming (Long-Term Passive Income)
🔹 Why It’s Profitable
- High-value crops that require low ongoing maintenance.
- Nuts and tree crops store well, allowing flexibility in sales.
- Global demand is rising for nuts, exotic fruits, and medicinal trees.
🔹 Most Profitable Nut & Tree Crops
✅ Almonds, walnuts, pecans, chestnuts, hazelnuts, avocados, olives, moringa trees.
🔹 Profit Potential
💰 High – Tree crops provide long-term passive revenue and fetch premium prices.
✅ Best For: Long-term investors, large-scale farms, regenerative agriculture.
7️⃣ Farm-to-Table & Direct-to-Consumer Sales (Higher Margins & Brand Loyalty)
🔹 Why It’s Profitable
- Cuts out middlemen, allowing farmers to keep more profit per sale.
- CSA (Community Supported Agriculture) memberships create recurring revenue.
- Consumers prefer buying directly from farmers for quality assurance.
🔹 Best Selling Direct-to-Consumer Products
✅ Fresh produce, organic meats, homemade jams, dairy, farm-fresh eggs, honey, baked goods.
🔹 Profit Potential
💰 Very High – DTC sales yield 30-50% more profit than wholesale.
✅ Best For: Farmers selling at farmers’ markets, subscription boxes, or online farm stores.
📊 Profitability Comparison Chart
| Farming Niche | Profitability | Scalability | Investment Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic & Specialty Crops | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | Medium |
| Livestock & Free-Range Farming | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | High |
| Medicinal & Herbal Farming | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | Low-Medium |
| Greenhouse Farming | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | High |
| Agritourism & Farm Experiences | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | Medium |
| Nut & Tree Farming | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | High |
| Direct-to-Consumer Sales | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | Low-Medium |
📌 Final Verdict: Best Profitable Farming Niches
✅ Highest Short-Term Profits: Direct-to-Consumer Sales, Agritourism, Organic Crops.
✅ Best for Long-Term Wealth: Nut & Tree Farming, Greenhouse Farming.
✅ Most Scalable Models: Greenhouse Farming, Direct-to-Consumer, Livestock Farming.
✅ Lowest Investment Startups: Herbal Farming, Farm-to-Table CSA Programs.
A combination of high-margin farming niches with direct sales and value-added products creates the most profitable farm business models. 🚜💰
🚜 Traditional Farming vs. Other Business Models
Farming is one of the oldest business models in human history, but modern entrepreneurs have more options than ever when choosing how to build wealth. Here’s how traditional farming compares to other business models in terms of profitability, scalability, automation, and risk.
🌾 Traditional Farming vs. E-Commerce (Selling Products Online)
✅ Key Differences:
- Farming requires land, equipment, and physical labor, while e-commerce can be run from anywhere with an internet connection.
- E-commerce scales faster by leveraging dropshipping, digital products, and online marketplaces.
- Farming produces tangible goods (fruits, vegetables, livestock), while e-commerce focuses on digital or physical product sales.
💰 Which is More Profitable?
- E-commerce has higher margins, less overhead, and fewer operational risks.
- Traditional farming has steady demand but is more capital-intensive and vulnerable to external factors like weather and regulations.
🏆 Winner for Fast Profits & Scalability: E-Commerce
🏆 Winner for Long-Term, Tangible Assets: Traditional Farming
🌾 Traditional Farming vs. Real Estate Investing
✅ Key Differences:
- Farming generates income through crop sales, livestock, and agritourism, while real estate investing earns through rent, appreciation, and property flipping.
- Land ownership in farming can be profitable over time, but real estate generally has higher appreciation rates and lower operational risk.
- Real estate offers passive income with rental properties, while farming requires ongoing labor and maintenance.
💰 Which is More Profitable?
- Real estate investing tends to yield better returns with less effort over time.
- Farming can be highly profitable, especially in organic or specialty markets, but requires active management.
🏆 Winner for Passive Income & Appreciation: Real Estate
🏆 Winner for Self-Sufficiency & Sustainable Living: Farming
🌾 Traditional Farming vs. Subscription-Based Business Models
✅ Key Differences:
- Subscription businesses create recurring revenue through memberships, while farming relies on seasonal and bulk sales.
- Farming income fluctuates with supply and demand, but subscriptions provide predictable monthly cash flow.
- Farmers can incorporate subscriptions through CSA (Community Supported Agriculture) programs or farm-based memberships.
💰 Which is More Profitable?
- Subscription models can generate consistent, recurring revenue without relying on external factors like weather or crop yields.
- Farming with a subscription component (CSA, farm memberships) can stabilize cash flow but still requires land and logistics.
🏆 Winner for Consistent Revenue: Subscription-Based Business
🏆 Winner for Tangible Products & Food Security: Farming
🌾 Traditional Farming vs. Digital Marketing & Affiliate Marketing
✅ Key Differences:
- Digital marketing is fully online, scalable, and can be automated, whereas farming requires manual labor, equipment, and physical space.
- Affiliate marketing earns commissions for promoting products, while farming earns through direct sales of crops, livestock, or farm experiences.
- Farming has operational challenges like pests, climate, and labor, while digital marketing has lower startup costs and higher automation potential.
💰 Which is More Profitable?
- Digital marketing can be scaled quickly, earning passive income with little overhead.
- Farming has long-term value but requires ongoing work and significant investment upfront.
🏆 Winner for Low Cost & Scalability: Digital Marketing
🏆 Winner for Tangible Product Creation: Farming
🌾 Traditional Farming vs. Investing in Stocks & Day Trading
✅ Key Differences:
- Farming builds long-term, sustainable wealth through land ownership and product sales.
- Stock market investing and day trading focus on capital growth and passive income without requiring physical assets.
- Investing is high-risk but can provide quick returns, whereas farming is more stable but requires patience.
💰 Which is More Profitable?
- Day trading has higher earning potential in the short term but comes with higher risk.
- Farming provides steady income, but profits depend on market prices, weather conditions, and crop yields.
🏆 Winner for Fast, Scalable Returns: Investing & Day Trading
🏆 Winner for Long-Term Sustainable Growth: Farming
📌 Final Verdict: Farming vs. Other Business Models
| Business Model | Startup Cost | Scalability | Profitability | Risk Level | Automation Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Farming | High | Medium | Medium-High | High | Low |
| E-Commerce | Low | High | High | Low-Medium | High |
| Real Estate Investing | Medium-High | High | High | Low-Medium | Medium |
| Subscription-Based Business | Low | Very High | High | Low | High |
| Digital Marketing & Affiliate Marketing | Very Low | Very High | High | Low | High |
| Stock Investing & Day Trading | Medium-High | High | High (if successful) | High | Medium |
✅ Best for Low-Cost, High-Profit Online Income: Affiliate Marketing & Subscription Business
✅ Best for Passive Wealth Building: Real Estate Investing & Stock Market
✅ Best for Physical, Land-Based Business: Farming & Real Estate
✅ Best for Quick Growth & Automation: E-Commerce & Digital Marketing
📌 Conclusion:
While traditional farming offers long-term sustainability, food security, and land ownership, it requires significant investment and active management. Compared to digital businesses, real estate, and investing, farming has more risks but provides real-world assets and diverse income opportunities.
The best approach? Combine farming with modern business models like direct-to-consumer e-commerce, agritourism, or subscription models to maximize profitability and long-term growth. 🚜💰
🌱 Future Trends in Traditional Farming Business
The agriculture industry is evolving rapidly with technological advancements, consumer demand shifts, and sustainability concerns shaping the future of farming. Here are the key trends that will define the next decade of traditional farming.
1️⃣ Smart Farming & Agricultural Technology (AgTech) 🚜📡
Technology is revolutionizing farming with precision agriculture, AI-driven analytics, and automation. Farmers are adopting:
✅ Drones & GPS Mapping – For precision planting, pest control, and irrigation management.
✅ IoT & Smart Sensors – To monitor soil health, moisture levels, and climate conditions.
✅ AI-Powered Data Analytics – To predict crop yields, optimize resources, and reduce waste.
📌 Why It Matters: Reduces costs, improves efficiency, and boosts yields.
2️⃣ Regenerative & Sustainable Agriculture 🌍♻️
Consumers and regulators are pushing for eco-friendly, climate-resilient farming practices. The future will favor:
✅ No-Till & Cover Cropping – Protects soil health and reduces erosion.
✅ Carbon Sequestration Farming – Incentives for farmers reducing carbon footprints.
✅ Water Conservation Methods – Efficient irrigation and drought-resistant crops.
📌 Why It Matters: Increases long-term farm viability while meeting sustainability goals.
3️⃣ Vertical & Urban Farming 🌆🌿
With growing urban populations, space-efficient farming is gaining traction. Emerging trends include:
✅ Vertical Farming & Hydroponics – Growing food in stacked layers indoors.
✅ Community-Based Urban Farms – Rooftop farms, community gardens, and localized food production.
✅ Farm-to-Table Restaurants – Restaurants integrating their own small-scale farms.
📌 Why It Matters: Meets urban food demand and reduces transportation costs.
4️⃣ Direct-to-Consumer & Farm E-Commerce 📦🛒
More farmers are bypassing traditional distribution channels and selling directly to consumers online. Growth areas include:
✅ Farm Subscription Boxes (CSA Programs) – Customers receive fresh produce weekly.
✅ E-Commerce for Farm Goods – Online marketplaces for organic produce, meats, and dairy.
✅ Farmers Using Social Media & Content Marketing – Engaging directly with consumers via Instagram, YouTube, and blogs.
📌 Why It Matters: Cuts out middlemen, increases profits, and builds brand loyalty.
5️⃣ Alternative Protein & Plant-Based Farming 🌾🍄
As demand for alternative proteins rises, farmers are shifting to:
✅ Hemp & Legume Farming – Used in plant-based meats and sustainable protein sources.
✅ Mushroom & Microgreen Farming – High-margin, space-efficient crops growing in popularity.
✅ Insect Farming – Emerging industry for protein-rich feed and food products.
📌 Why It Matters: Expands revenue opportunities beyond traditional crops and livestock.
6️⃣ Blockchain & Supply Chain Transparency 🔗📊
Consumers demand traceability in food production, leading to:
✅ Blockchain for Farm-to-Fork Transparency – Secure, trackable food sourcing data.
✅ Smart Contracts for Fair Pricing – Reducing middlemen and improving farmer profits.
✅ Digital Farm Certification & Labeling – Verifiable organic, non-GMO, and sustainable credentials.
📌 Why It Matters: Builds trust with consumers and ensures fair trade for farmers.
7️⃣ Government Policies & Carbon Credits 🌱💵
Governments worldwide are incentivizing sustainable agriculture with:
✅ Subsidies for Eco-Friendly Farming Practices – Funding regenerative and organic practices.
✅ Carbon Credit Programs – Farmers can earn money for adopting climate-smart practices.
✅ Regenerative Agriculture Tax Benefits – Incentives for reducing environmental impact.
📌 Why It Matters: Encourages sustainability while providing financial benefits to farmers.
📌 Final Thoughts: The Future of Traditional Farming
🚀 Farming is evolving from a labor-intensive industry to a high-tech, data-driven business.
🔗 Farmers who adapt to digital sales, automation, and sustainability will thrive.
💰 Diversifying revenue with e-commerce, agritourism, and alternative crops will increase profitability.
✅ Best Long-Term Trends: AgTech, direct-to-consumer sales, sustainable practices.
✅ Best for Profitability: Alternative proteins, urban farming, blockchain-enabled supply chains.
✅ Best for Small Farmers: Subscription-based CSA models, niche organic crops, and e-commerce.
🌱 The future of farming is digital, sustainable, and more profitable than ever. 🚜
Updates on
Traditional Farming Business
Get notified on new updates with the
Traditional Farming Business ecosystem.
Sponsor
Reviews of Traditional Farming Business Landscape
https://www.gezesrkog.com/
Dear,
I hope this email finds you well. I’m excited to introduce you to Cargoholidays.com, your gateway to a unique and adventurous way of exploring the world through cargo ship travel. As a leading cargo travel agency, we specialize in creating unforgettable journeys that offer a fresh perspective on travel and adventure.
At CargoHolidays, we understand that traditional travel experiences may not be for everyone, and that’s why we offer an alternative that’s both enriching and fascinating. Our cargo ship travel services open up a world of possibilities for those seeking a truly authentic and immersive travel experience.
I invite you to explore our website at CargoHolidays Website to browse our available routes at cargoholidays.com, destinations, and testimonials from fellow adventurers who have experienced the magic of cargo ship travel with us.
If you’re ready to embark on a one-of-a-kind journey or have any questions about our services, please don’t hesitate to contact us at contact@cargoholidays.com. Our dedicated team is here to assist you in planning your cargo ship adventure, providing insights, and addressing any queries you may have.
Safe travels and warm regards,